Troubleshooting Questions
Question 1
Explanation
A late collision is defined as any collision that occurs after the first 512 bits of the frame have been transmitted. The usual possible causes are full-duplex/half-duplex mismatch, exceeded Ethernet cable length limits, or defective hardware such as incorrect cabling, non-compliant number of hubs in the network, or a bad NIC.
We can check the interface counter with the “show interface <interface>” command on a Cisco device. For example:
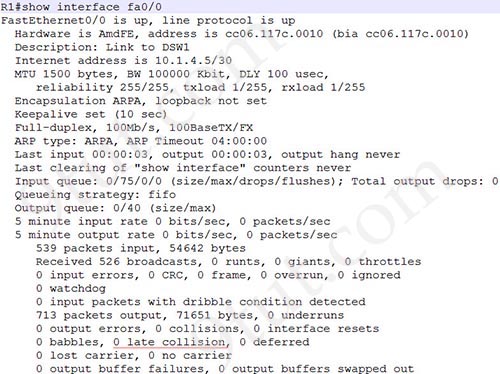
On an Ethernet connection, a duplex mismatch is a condition where two connected devices operate in different duplex modes, that is, one operates in half duplex while the other one operates in full duplex.
Note:
+ Runts are frames which do not meet the minimum frame size of 64 bytes. Runts are usually created by collisions.
+ Giants: frames that are larger than 1,518 bytes
Question 2
Explanation
The ports on the switch are not up indicating it is a layer 1 (physical) problem so we should check cable type, power and how they are plugged in.
Question 3
Question 4
Question 5
Question 6
Explanation
Explanation
The “show ip nat statistics” only gives us information about NAT translation. We cannot know if IP routing is enabled or the VLANs are up not not.
The “show ip statistics” command does not exist.
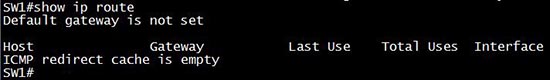
With the “show ip interface brief” we can see if the interface VLANs are up or not but cannot see if IP routing is enabled or not. So let’s see what information can be learned with the “show ip route” command.
By using the command “show ip route” we will learn if IP routing is enabled. If it is not enabled we will see this output:
After enabling ip routing (via the “ip routing” in global configuration mode) we can see all the interfaces. For example:
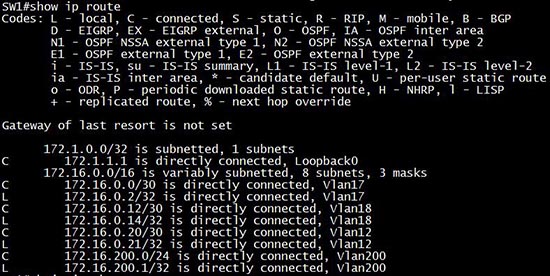
If we shut down an interface VLAN (Vlan18)
Sw1(config)#interface vlan 18
Sw1(config-if)#shutdown
then we will not see it in the routing table any more.
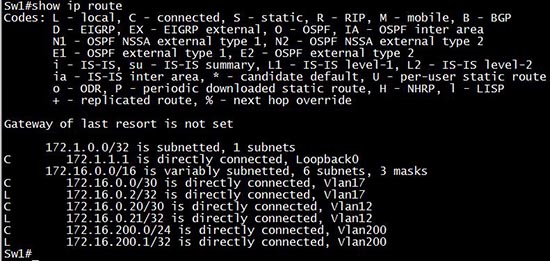
Therefore if the statement “local VLANs are up” means “the interface VLANs are up” then the “show ip route” is the best answer in this case.
Note: The IOS used to test is IOSv15.1
Question 7
Explanation
In fact all three of the above answers are in the problem-solving process but “gather facts” is at Step 2 while “Create an action plan” and “Implement an action plan” is at step 4 & 5 of this link http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1901.html
Step 2 Gather the facts that you need to help isolate possible causes.
Ask questions of affected users, network administrators, managers, and other key people. Collect information from sources such as network management systems, protocol analyzer traces, output from router diagnostic commands, or software release notes.
Question 8
Explanation
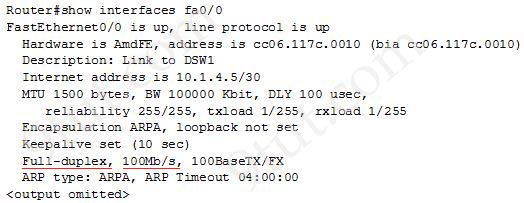
The “show interfaces …” command gives us information about speed and duplex mode of the interface. In the output below, the link speed is 100Mbps and it is working in Full-duplex mode.
Question 9
Question 10
Explanation
To check the connectivity between a host and a destination (through some networks) we can use both “tracert” and “ping” commands. But the difference between these two commands is the “tracert” command can display a list of near-side router interfaces in the path between the source and the destination. In this question the PC and the host are in the same VLAN so “tracert” command is not useful as there is no router to go through. Therefore the best answer in this case is “ping address”.
Note: “traceroute” command has the same function of the “tracert” command but it is used on Cisco routers only, not on a PC.
Question 11
Explanation
Complete these steps to troubleshoot this problem:
Ensure the router can reach the DNS server. Ping the DNS server from the router using its IP address, and make sure that the ip name-server command is used to configure the IP address of the DNS server on the router.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/domain-name-system-dns/24182-reversedns.html
Question 12
Explanation
The extended traceroute command can be used by typing only “traceroute” keyword on the device as follows:
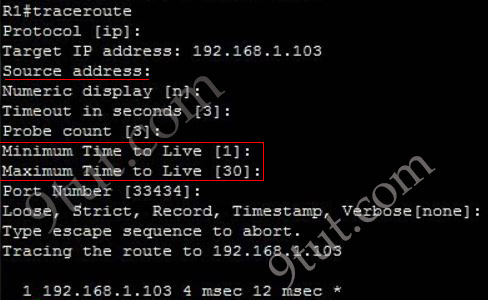
We can specify a source address (which can be a specific IP address or interface on that device). We can also specify a Time to Live value of each packet sent.
Question 13
Explanation
A late collision is defined as any collision that occurs after the first 512 bits of the frame have been transmitted. The usual possible causes are full-duplex/half-duplex mismatch, exceeded Ethernet cable length limits, or defective hardware such as incorrect cabling, non-compliant number of hubs in the network, or a bad NIC.
Note: On an Ethernet connection, a duplex mismatch is a condition where two connected devices operate in different duplex modes, that is, one operates in half duplex while the other one operates in full duplex.
Duplex mismatch would not cause the link to be down/down, but would only result in poor performance like increase late collisions on the interface.
Question 14
Explanation
From this paragraph:
Step 2. Resolve or escalate: Problem isolation should eventually uncover the root cause of the problem – that is, the cause which, if fixed, will resolve the problem. In short, resolving the problem means finding the root cause of the problem and fixing that problem. Of course, what do you do if you cannot find the root cause, or fix (resolve) that root cause once found? Escalate the problem. Most companies have a defined escalation process, with different levels of technical support and management support depending on whether the next step requires more technical expertise or management decision making.
Reference: ICND1 100-105 Official Cert Guide
Also from this link: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=1578504&seqNum=2
“After you have clearly defined the problem, you have one more step to take before starting the actual troubleshooting process. You must determine whether this problem is your responsibility or if it needs to be escalated to another department or person. For example, assume the reported problem is this: “When user Y tries to access the corporate directory on the company intranet, she gets a message that says permission is denied. She can access all other intranet pages.” You are a network engineer, and you do not have access to the servers. A separate department in your company manages the intranet servers. Therefore, you must know what to do when this type of problem is reported to you as a network problem. You must know whether to start troubleshooting or to escalate it to the server department. It is important that you know which type of problems is your responsibility to act on, what minimal actions you need to take before you escalate a problem, and how you escalate a problem.”
So we can say answer A is the most suitable choice.


