Cloud & Virtual Services
|
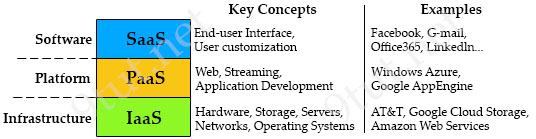
Cloud & Virtual Services Quick Summary Three cloud supporting services cloud providers provide to customer: + SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS uses the web to deliver applications that are managed by a third-party vendor and whose interface is accessed on the clients’ side. Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser without any downloads or installations required, although some require plugins.
|
Question 1
Question 2
Explanation
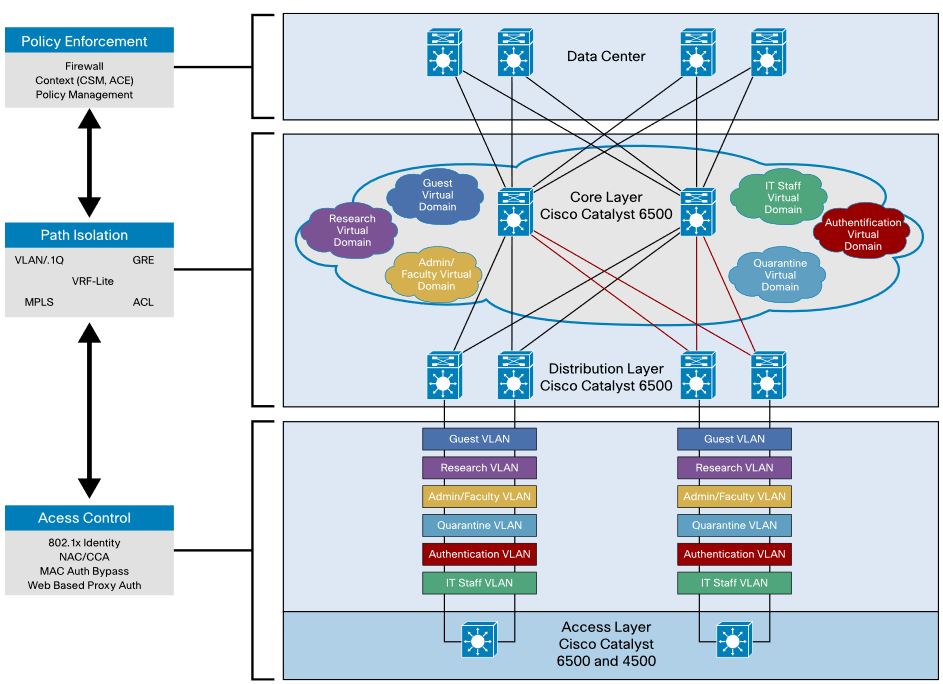
Network virtualization architecture has three main components:
+ Network access control and segmentation of classes of users: Users are authenticated and either allowed or denied into a logical partition. Users a
re segmented into employees, contractors and consultants, and guests, with respective access to IT assets. This component identifies users who are authorized to access the network and then places them into the appropriate logical partition.
+ Path isolation: Network isolation is preserved across the entire enterprise: from the edge to the campus to the WAN and back again. This component maintains traffic partitioned over a routed infrastructure and transports traffic over and between isolated partitions. The function of mapping isolated paths to VLANs and to virtual services is also performed in component.
+ Network Services virtualization: This component provides access to shared or dedicated network services such as security, quality of service (QoS), and address management (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol [DHCP] and Domain Name System [DNS]). It also applies policy per partition and isolates application environments, if required.
Question 3
Explanation
Four technical services are essential to supporting the high level of flexibility, resource availability, and transparent resource connectivity required for cloud computing:
+ The Layer 3 network offers the traditional routed interconnection between remote sites and provides end-user access to cloud services.
+ The extended LAN between two or more sites offers transparent transport and supports application and operating system mobility.
+ Extended SAN services support data access and accurate data replication.
+ IP Localization improves northbound and southbound traffic as well as server-to-server workflows.
Question 4
Explanation
Network virtualization architecture has three main components:
+ Network access control and segmentation of classes of users: Users are authenticated and either allowed or denied into a logical partition. Users are segmented into employees, contractors and consultants, and guests, with respective access to IT assets. This component identifies users who are authorized to access the network and then places them into the appropriate logical partition.
+ Path isolation: Network isolation is preserved across the entire enterprise: from the edge to the campus to the WAN and back again. This component maintains traffic partitioned over a routed infrastructure and transports traffic over and between isolated partitions. The function of mapping isolated paths to VLANs and to virtual services is also performed in component.
+ Network Services virtualization: This component provides access to shared or dedicated network services such as security, quality of service (QoS), and address management (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol [DHCP] and Domain Name System [DNS]). It also applies policy per partition and isolates application environments, if required.
Question 5
Explanation
Network virtualization architecture has three main components:
+ Network access control and segmentation of classes of users: Users are authenticated and either allowed or denied into a logical partition. Users are segmented into employees, contractors and consultants, and guests, with respective access to IT assets. This component identifies users who are authorized to access the network and then places them into the appropriate logical partition.
+ Path isolation: Network isolation is preserved across the entire enterprise: from the edge to the campus to the WAN and back again. This component maintains traffic partitioned over a routed infrastructure and transports traffic over and between isolated partitions. The function of mapping isolated paths to VLANs and to virtual services is also performed in component.
+ Network Services virtualization: This component provides access to shared or dedicated network services such as security, quality of service (QoS), and address management (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol [DHCP] and Domain Name System [DNS]). It also applies policy per partition and isolates application environments, if required.
Question 6
Explanation
Below are the 3 cloud supporting services cloud providers provide to customer:
+ SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS uses the web to deliver applications that are managed by a third-party vendor and whose interface is accessed on the clients’ side. Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser without any downloads or installations required, although some require plugins.
+ PaaS (Platform as a Service): are used for applications, and other development, while providing cloud components to software. What developers gain with PaaS is a framework they can build upon to develop or customize applications. PaaS makes the development, testing, and deployment of applications quick, simple, and cost-effective. With this technology, enterprise operations, or a third-party provider, can manage OSes, virtualization, servers, storage, networking, and the PaaS software itself. Developers, however, manage the applications.
+ IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): self-service models for accessing, monitoring, and managing remote datacenter infrastructures, such as compute (virtualized or bare metal), storage, networking, and networking services (e.g. firewalls). Instead of having to purchase hardware outright, users can purchase IaaS based on consumption, similar to electricity or other utility billing.
Reference: https://apprenda.com/library/paas/iaas-paas-saas-explained-compared/
In the context of the three cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS and SaaS), DNS can be considered an IaaS service.
Reference: http://searchcloudsecurity.techtarget.com/tip/DNS-attacks-Compromising-DNS-in-the-cloud



D. platform-as-a-service
can someone send me the current ccna 200-125 dumps please! email is edgarc2708@ gmail. com
I tried the 451 Cloud, have failed 2 times. The exam dumps are all not valid I used Lead to Pass as well as the ete files, nothing, and I wonder why?
The questions were exactly the same on my too attempts but all the answers on the dump and the books i believe that are wrong.
Hi!
I failed my canna test 1 composite. so the question is, if I take the exam again, it will be the same test?
thanks in advanced!