EIGRP Questions
Note: If you are not sure about EIGRP, please read our EIGRP Tutorial.
Question 1
Explanation
Below is an example of the “show ip eigrp neighbors” output.
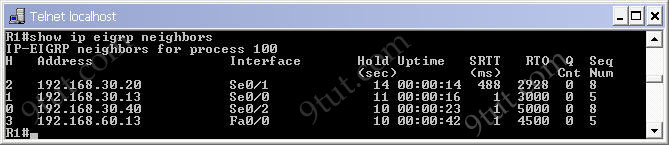
Let’s analyze these columns:
+ H: lists the neighbors in the order this router was learned
+ Address: the IP address of the neighbors
+ Interface: the interface of the local router on which this Hello packet was received
+ Hold (sec): the amount of time left before neighbor is considered in “down” status
+ Uptime: amount of time since the adjacency was established
+ SRTT (Smooth Round Trip Timer): the average time in milliseconds between the transmission of a packet to a neighbor and the receipt of an acknowledgement.
+ RTO (Retransmission Timeout): if a multicast has failed, then a unicast is sent to that particular router, the RTO is the time in milliseconds that the router waits for an acknowledgement of that unicast.
+ Queue count (Q Cnt): shows the number of queued EIGRP packets. It is usually 0.
+ Sequence Number (Seq Num): the sequence number of the last update EIGRP packet received. Each update message is given a sequence number, and the received ACK should have the same sequence number. The next update message to that neighbor will use Seq Num + 1.
In this question we have to check the RTO and Q cnt fields.
Question 2
Explanation
To configure EIGRP for IPv6 we must explicitly specify a router ID before it can start running. For example:
| ipv6 router eigrp 1 eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2 no shutdown |
Notice that EIGRP for IPv6 router-id must be an IPv4 address. EIGRP for IPv4 can automatically pick-up an IPv4 to use as its EIGRP router-id with this rule:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback interface is selected as the router ID.
+ If there are not any loopback addresses configured, the highest IP address assigned to any other active interface is chosen as the router ID
EIGRPv3 also uses the AS number (for example: ipv6 eigrp 1 under interface mode).
Question 3
Explanation
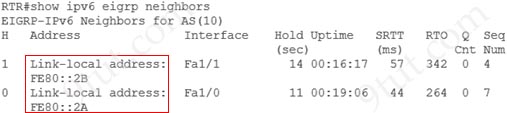
The “show ipv6 eigrp neighbors” command displays the neighbors discovered by the EIGRPv6. Notice that the neighbors are displayed by their link-local addresses.
Question 4
Explanation
The goodbye message is a feature designed to improve EIGRP network convergence. The goodbye message is broadcast when an EIGRP routing process is shutdown to inform adjacent peers about the impending topology change. This feature allows supporting EIGRP peers to synchronize and recalculate neighbor relationships more efficiently than would occur if the peers discovered the topology change after the hold timer expired.
The following message is displayed by routers that run a supported release when a goodbye message is received:
| *Apr 26 13:48:42.523: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: IP-EIGRP(0) 1: Neighbor 10.1.1.1 (Ethernet0/0) is down: Interface Goodbye received |
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/ip/configuration/guide/fipr_c/1cfeigrp.html
Note: In this question we should understand “impending”, not “implementing” as there are no correct answers with “implementing” topology change.
Question 5
Explanation
With auto-summary feature is turned on, EIGRP will summary these networks to their classful networks automatically. For example:
+ 172.15.4.0 belongs to class B so it will be summarized to 172.15.0.0
+ 10.4.3.0 belongs to class A so it will be summarized to 10.0.0.0
+ 192.168.4.0 belongs to class C so it will be summarized to 192.168.4.0 (same)
Question 6
Explanation
Split horizon is used in distance vector routing protocols (like RIP, EIGRP) to prevent routing loops by prohibiting a router from advertising a route back to the interface from which it was learned.
Question 7
Explanation
EIGRP provides a mechanism to load balance over unequal cost paths (or called unequal cost load balancing) through the “variance” command. In other words, EIGRP will install all paths with metric < variance * best_metric into the local routing table, provided that it meets the feasibility condition (to prevent routing loop). The feasibility condition states that, the Advertised Distance (AD) of a route must be lower than the feasible distance of the current successor route.
Question 8
Explanation
EIGRP provides a mechanism to load balance over unequal cost paths (or called unequal cost load balancing) through the “variance” command. In other words, EIGRP will install all paths with metric < variance * best_metric into the local routing table, provided that it meets the feasibility condition (to prevent routing loop). The feasibility condition states that, the Advertised Distance (AD) of a route must be lower than the feasible distance of the current successor route.
Question 9
Explanation
From the routing table we learn that network 192.168.10.0/30 is learned via 2 equal-cost paths (192.168.10.9 &192.168.10.5) -> traffic to this network will be load-balancing.
Question 10
Explanation
This is an example of how to configure EIGRP for IPv6:
| interface Serial0/0 no ip address ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2010:AB8::1/64 ipv6 enable ipv6 eigrp 1 ! ipv6 router eigrp 1 eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2 no shutdown |
As you can see, EIGRP for IPv6 can only be enabled under each interface -> A is correct.
Under EIGRP process there is a shutdown feature where you can turn on or off -> E is correct.
Question 11
Explanation
These networks will be summarized to the major networks of that class so:
+ 10.4.3.0 belongs to class A -> It will be summarized into 10.0.0.0
+ 172.16.4.0 belongs to class B -> It will be summarized into 172.16.0.0
+ 192.168.2.0 belongs to class C -> It will be summarized into 192.168.2.0 (not changed)
Question 12
Question 13
Question 14
Explanation
The command “ipv6 summary-address eigrp as-numberipv6-address [admin-distance]” can be used to configure a summary aggregate address for a specified interface. We can also configure the administrative distance of that summary aggregate address as well.
Note: The “ipv6 bandwidth-percent eigrp” command configures the percentage of bandwidth that may be used by EIGRP for IPv6 on an interface. By default, EIGRP packets consume a maximum of 50 percent of the link bandwidth.
EIGRP for IPv6 uses the minimum bandwidth on the path to a destination network and the total delay to compute routing metrics. You can use the metric weights command to adjust the default behavior of EIGRP for IPv6 routing and metric computations.


