IP Routing
Question 1
Explanation
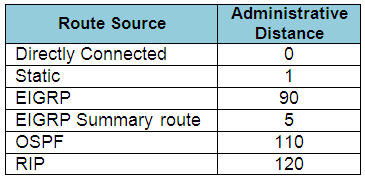
When one route is advertised by more than one routing protocol, the router will choose to use the routing protocol which has lowest Administrative Distance. The Administrative Distances of popular routing protocols are listed below:
Question 2
Explanation
The simple syntax of static route:
ip route destination-network-address subnet-mask {next-hop-IP-address | exit-interface}
+ destination-network-address: destination network address of the remote network
+ subnet mask: subnet mask of the destination network
+ next-hop-IP-address: the IP address of the receiving interface on the next-hop router
+ exit-interface: the local interface of this router where the packets will go out
In the statement “ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.240.0 GigabitEthernet0/1″:
+ 192.168.0.0 255.255.240.0: the destination network
+ GigabitEthernet0/1: the exit-interface
Question 3
Question 4
Explanation
The static routing specifies a fixed destination so it is “consistent”. It is best used for small-scaled places where there are a few routers only. When links fail, static route cannot automatically find an alternative path like dynamic routing so routing is disrupted.
Question 5
Explanation
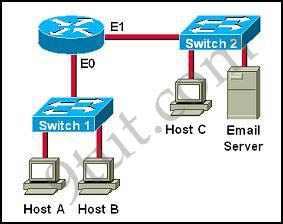
Host Z will use ARP to get the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to it and use this MAC as the destination MAC address. It use the IP address of the storage server as the destination IP address.
For example in the topology below, host A will use the MAC address of E0 interface of the router as its destination MAC address to reach the Email Server.
Question 6
Explanation
The Administrative Distance (AD) of popular routing protocols is shown below. You should learn them by heart:

Note: The AD of iBGP is 200
The smaller the AD is, the better it is. The router will choose the routing protocol with smallest AD.
In this case EIGRP with AD of 90 is the smallest one.
Question 7
Question 8
Question 9
Explanation
The Layer 2 information (source and destination MAC) would be changed when passing through each router. The Layer 3 information (source and destination IP addresses) remains unchanged.
Question 10
Question 11



Question 8:
I would also think, that the correct answer is B, because in the routing table there are no network masks. There are Prefixes. But nearly on all Websites with this question, D is written to be the correct answer?!
@Lywa
i am agree . B suppose to be right.